What is a Muffler?
Mufflers are of the main components found in automotive exhaust systems. The primary purpose of this component is to reduce the noise level of the exhaust stream in any vehicle that has an internal combustion engine. Conventional gasoline engines, diesel engines, flex fuel, and hybrid electric engines all use mufflers to reduce the exhaust noise to an acceptable level. In addition to this reduction in noise level, some mufflers also serve other aesthetic or performance-related purposes.
Contents
History of the Muffler
The engines of the first automobiles were smaller and less powerful than they are today, so they weren’t nearly as loud during operation. Much like the small engines found in lawn mowers and similar equipment today, those early automobiles lacked any sort of exhaust silencing devices.
Although they weren’t as loud as modern engines, unrestricted exhaust noise did pose several issues, which included noise complaints and conflicts with the horse-drawn carriage that early cars shared the road with. Hobbyists and automakers alike examined this issue from very early on, and the first patent for a muffler was issued in 1897.
Milton Reeves is credited with inventing the first muffler, according to US patent number 582485. This patent describes a component that is composed of multiple concentric shells that were designed to “expand the exhaust product gradually.” Although Reeves’ patent was specifically for a motorcycle muffler, similar designs would also be used on automobiles.
How do Mufflers Work?
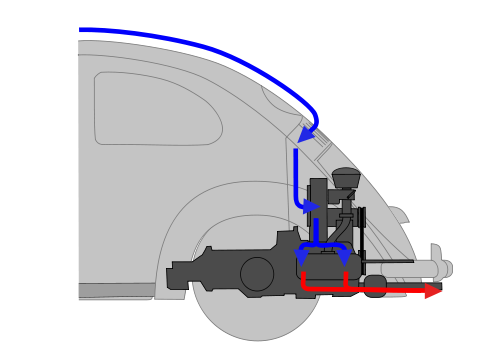
When an exhaust stream first leaves an engine, it is extremely loud and incredibly hot. By the time it leaves the tailpipe, it is significantly quieter and cooler. Although heat is lost throughout the exhaust system, the component that is responsible for the majority of the sound reduction is the muffler.
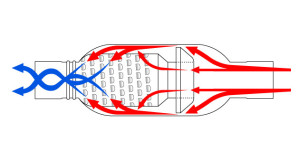
There are a handful of different types of mufflers, and they all use somewhat different sound deadening techniques. However, all mufflers work by essentially cancelling out some of the sound waves created by the exhaust stream through the process of destructive interference. Regardless of the specific method that a muffler uses, the result is a significantly quieter exhaust stream at the tailpipe.
One common muffler design utilizes a series of tubes and chambers inside the main body of the component. The inlet tube is not connected directly to the outlet tube, which prevents exhaust from simply passing through the muffler. Instead, the inlet and outlet pipes have perforations that force the exhaust stream to break up and pass through one or more resonating chambers. When everything is working properly, the resonating chamber creates sound waves that are cancelled out by the incoming exhaust stream.
The Downside of Mufflers
Although mufflers are great at reducing the sound level of exhaust, that functionality doesn’t come without a price. The issue is that any restriction on the exhaust stream of an internal combustion effectively reduces its efficiency. To that end, mufflers are typically designed to provide an acceptable balance between desirable sound reduction and undesirable power reduction.
Performance Mufflers
Since power reduction isn’t always acceptable, a variety of performance mufflers are available from the aftermarket. Some types of high performance mufflers include:
- glass packs
- louvered core
- perforated core
- spiral baffle
- turbine
Unlike traditional mufflers, performance mufflers are designed to reduce sound levels and provide the least amount of exhaust restriction possible. Each variation achieves this in a different way. For instance, turbine-style mufflers actually use partial vacuum to create negative exhaust back pressure.
In addition to performance mufflers, it is also possible to simply remove the muffler in order to improve performance or gas mileage. This results in significantly louder exhaust, and it is actually illegal in some areas. Some aftermarket “mufflers” that produce too much noise are illegal for the same reasons.
Muffler Failure
Mufflers typically fail due to rust, and it’s fairly common for these components to rust from the inside out. This is due to the fact that moisture can accumulate within the internal pipes and chambers, which eventually causes the metal to rust. In many cases, these internal components will disintegrate while the exterior shell remains relatively unscathed.
In addition to internal and external rust issues, mufflers can also fail if the internal components fail either due to manufacturing defects or simple age. In either case, the fix is typically to replace the muffler. Unless the unit is welded in place, it is typically possible to replace a muffler without replacing any other exhaust system components.